VSCode调试C/C++项目
VS Code作为宇宙第一编辑器,在众多插件的加持下,具有了调试、单元测试等等功能,使其越来越像一个IDE。
然而很多人其实并不会使用VS Code的调试功能,只是把VS Code当做了一个带有语法补全的编辑器。这实际上极大地浪费了VS Code的功能,尤其是对于C/C++开发者来说,使用命令行的GDB调试远不如使用VS Code内嵌的GDB图形化界面调试来的舒服。
本文就讲介绍如何使用VS Code调试C/C++项目
1. 概述
通常我们在调试一个C/C++工程的时候,大体上的流程可以分为两步:
- 启动调试器(GDB)前的准备工作
- 启动调试器(GDB)进行调试
例如对于一个CMake组织的C/C++项目,这两大步具体包含的流程如下(编写CMakeLists.txt是在编码阶段,编码是与调试独立的阶段):
- 启动调试器(GDB)前的准备工作
- 创建
build文件夹:mkdir -p build - 切换到
build文件夹:cd build - 配置(Configure)项目:
cmake .. <option> - 构建/编译(Build)项目:
make
- 创建
- 启动调试器(GDB)进行调试
- 启动调试器:
gdb <path-to-executable
- 启动调试器:
对于不同的项目(npm项目、C#项目、java项目等等),可能在启动调试器前的准备工作不同,但是大体上都可以分为进行调试前需要进行的一系列任务,以及结合具体参数启动时调试器
因此,对于这两个阶段,VSCode中提供了tasks.json和launch.json两个文件来分别描述调试前的准备工作以及以指定的参数启动调试器
2. 调试前的准备工作:tasks.json
VSCode使用tasks.json来描述启动调试前的准备工作。
A. tasks.json的结构
tasks.json的结构一般如下
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
],
"inputs": [
]
}

B. version标签
version标签指定了Tasks.json的版本,因为不同的版本支持的标签不一样,所以需要使用version标签指明版本。
目前version支持2.0.0版本,所以直接指定version为2.0.0即可。
C. tasks标签
tasks标签是一个列表,我们在其中定义不同的task,而关于具体的task如何定义则见下
我们以创建build文件夹这个任务为例
{
"label": "create dir",
"type": "shell",
"command": "mkdir",
"args": [
"-p",
"build"
],
"windows": {
"args": [
"-Force",
"build"
],
"options": {
"shell": {
"executable": "powershell.exe"
}
},
}
}
1) label标签
label标签定义了一个任务的名字,稍后我们能用通过名字取定位一个任务,从而实现诸如将多个任务合并为一个组,而后执行一组任务这样的操作。
label标签的值是随我们自己喜欢,想写什么就写什么的。
2) type标签
type标签指定了一个任务的类型。所有的任务大致上可以分为两类:
- 第一类就是在
Shell中执行的命令,值为shell - 第二类就是一个进程,例如我们写的程序是操作
MySQL数据库的程序,那么就需要在调试前启动MySQL数据库,则此时MySQL数据库就是进程形式的任务。进程形式的任务的值为process
3 ) command标签
command标签指定了需要执行的命令或者程序。
- 如果是
Shell中的命令的话,那么command的值为需要执行的命令。 - 如果是进程的话,那么
command的值为需要执行的可执行程序的位置,可执行程序可以是有x权限的.sh,也可以是.exe等可执行程序。
4 ) args标签
args标签指定了执行的命令或者程序时传入的命令行参数。在具体执行的时候会把多个参数用空格连接起来而后执行。
结合command标签,我们执行的命令就是下面这句话
mkdir -p build
5 ) windows标签
windows标签指定了只有在windows系统上的配置。我们在windows标签中指定了两个标签options标签和args标签。
对于
args标签就意味着在其他系统(Linux/MacOS)上,使用-p build作为命令行参数,而在Windows系统上,使用-Force build作为命令行参数。这是因为在
Linux/MacOS系统上,创建一个文件夹使用下面的命令就行了mkdir -p 文件夹名但是在
Windows平台上,创建一个文件夹需要使用下面的命令mkdir -Force 文件夹名对于
options标签就意味着只有在Windows平台上才会有这个标签。
6 ) options标签
options标签指明了运行命令的shell的位置(shell标签)、运行命令的环境变量(env标签)以及运行命令的文件夹(cwd标签)。当然这里只用了shell这一个标签。
使用shell标签的原因是因为在Windows上有两个命令行,一个是cmd一个是powershell。而mkdir这个命令是在powershell中的,因此我们需要特殊指明在Windwos上需要使用powershell.exe作为Shell的解释器
D. input标签
input标签用于生成一个选项卡,接收用户的输入,一般是和args标签一起使用我们稍后再讲解这个标签的用法。
3. 启动调试器:launch.json
A. launch.json的结构
launch.json的结构一般如下
{
// 使用 IntelliSense 了解相关属性。
// 悬停以查看现有属性的描述。
// 欲了解更多信息,请访问: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"type": "gdb",
"request": "launch",
"name": "GDB",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/${command:AskForProgramName}",
"stopOnEntry": true,
"arguments": "",
"preLaunchTask": ""
}
]
}

B. version标签
launch.json中的version标签和tasks.json中的version标签作用是一样的,一般都用0.2.0。
C. configuration标签
configuration标签中定义了开始启动调试器时候的具体的配置信息。具体来说,可以有多套配置信息。即configuration标签下可以有多个条目。
1 ) name标签
name标签定义了一套配置信息的名称,这个名称稍后可以在左边的运行与调试页面中看到。

2 ) type标签
type标签指定了调试时启动的调试器:
对于
C/C++项目来说,type的值指定为cppdbg或者是cppvsdbg- 在
Windows上开发一般用的编译器都是Visual Studio中自带的msvc编译器,适用的调试器也是Visual Studio自带的,此时就需要把值设为cppvsdbg `Linux上用的一般都是gcc,MacOS上用的编译器一般都是clang,对应的调试器分别是gdb和lldb,此时需要把值设为`cppdbg
- 在
对于
Python项目来说,type的值指定为python,因为python解释器自带了pdb这个调试器- …
剩下的具体查询手册:https://code.visualstudio.com/docs
3 ) request标签
request标签指明了调试器调试程序的方式。具体来说有两种:
launch:表示调试器直接启动程序进行调试,类似于使用命令gdb helloworld,将会直接运行命令helloworldattach:有时候,我们需要调试的程序运行在远程服务器上,此时在服务器上已经运行了一个gdb,而且服务器上的gdb把调试服务暴露在某一个端口上,此时我们在本机上运行gdb的时候,通过链接远程服务器该端口,从而实现用本地的gdb调试远程服务器上的程序。此时,远程服务器上的gdb称为gdb server。这种调试方式称为attach,即把调试器附加到一个gdb server上去。
一般在本机做调试的时候值都是launch。
4 ) program标签
program标签指定了我们需要调试的程序。注意,如果request标签的值是attach的话,那么就不能使用program标签。
5 ) workspaceFolder宏
CMake中有EXECUTABLE_OUTPUT_PATH宏,我们可以指定EXECUTABLE_OUTPUT_PATH宏的值从而指定可执行文件输出的路径,也可以通过${}来读取EXECUTABLE_OUTPUT_PATH宏的值来打印到屏幕上或者用于为其他宏赋值。
类似的,VSCode中也有功能类似的宏,workspaceFolder这个宏就表示了当前打开的目录。我们也可以使用${}来获取这个宏的值。
6 ) command:AskForProgramName
command:AskForProgramName这个宏的作用就是在程序运行的时候在上面弹出来一个选项卡,询问用户需要调试的程序的名字。
例如我们直接对着launch.json这个程序按下F5,然后就会弹出来一个选项卡让我们输入需要调试的程序的名字

7 ) stopAtEntry标签
stopAtEntry标签表示在进入到主程序之后就会停下来,对于C/C++来说就是在进入main之后就停下来。
但是一般我们都是打上断点,然后直接运行到断点处,所以这个stopAtEntry的值一般用的都是false。
8 ) Arguments标签
这个标签我没用过,所以我也搞不清楚,如果要传参的给程序的话,用args标签
9 ) preLaunchTask标签
preLaunchTask标签可以说是最重要的标签之一,它沟通了launch.json和tasks.json这两个文件。
前面我们在tasks.json中定义了一系列任务,而launch.json中的这个标签说明了在启动调试器前需要执行的tasks.json中的那个任务。
所以利用这个标签,我们就可以实现从调试前的准备工作再到启动调试器这一连串的任务。
4. 一个Toy Example: echo 宏
下面展示一个Toy Example来展示tasks.json和launch.json的workflow
A. tasks.json的内容
Toy Example中tasks.json的内容如下
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "example",
"command": "echo",
"args": [
"${file}\n",
"${fileBasename}\n",
"${fileBasenameNoExtension}\n",
"${fileDirname}\n",
]
}
]
}
具体来说我们就是想要执行一下下面的命令
echo "${file}\n" "${fileBasename}\n" "${fileBasenameNoExtension}\n" "${fileDirname}\n"
主要是看一看这四个宏的值分别是什么
B. launch.json的内容
Toy Example中lauch.json的内容如下
{
// 使用 IntelliSense 了解相关属性。
// 悬停以查看现有属性的描述。
// 欲了解更多信息,请访问: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"type": "gdb",
"request": "launch",
"name": "Toy Example",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/${file}",
"stopOnEntry": true,
"preLaunchTask": "example"
}
]
}
具体来说就是在启动调试器之前运行一下上面定义的example这个task。
C. hello_world.c
我们接下来写一个hello_world.c,里面的内容如下:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
for (int i = 0; i < argc; i++)
printf("%s\n", argv[i]);
printf("Hello World!\n");
return 0;
}
D. 开始调试
首先在运行和调试界面把调试的配置选定为Toy Example,然后编辑器打开hello_world.c

接下来按F5开始调试
此时我们在终端就能够看到执行的任务以及输出

很清楚就能看到,上面四个宏的值分别是
${file} : /Users/jack/project/test/vscode_test/hello_world.c
${fileBasename} : hello_world.c
${fileBasenameNoExtension} : hello_world
${fileDirname} : /Users/jack/project/test/vscode_test
5. 一个Toy Example:编译文件
我们对上面的Toy Example进行修改,增加一个自动编译的功能
A. tasks.json的内容
我们给tasks.json新加一个task,即自动编译,此外我们修改一下输出宏的task
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "echo",
"command": "echo",
"args": [
"${file}\n",
"${pathSeparator}\n",
"${fileBasenameNoExtension}\n",
"${fileDirname}${pathSeparator}${fileBasenameNoExtension}.o\n"
]
},
{
"label": "build",
"command": "gcc",
"args": [
"${file}",
"-o",
"${fileDirname}${pathSeparator}${fileBasenameNoExtension}.o"
]
}
]
}
B. launch.json的内容
我们再给launch.json中新加一个配置信息
{
// 使用 IntelliSense 了解相关属性。
// 悬停以查看现有属性的描述。
// 欲了解更多信息,请访问: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"type": "gdb",
"request": "launch",
"name": "Echo Macros",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/${file}",
"stopOnEntry": true,
"preLaunchTask": "echo"
},
{
"type": "gdb",
"request": "launch",
"name": "Gcc Compile",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}${pathSeparator}${fileBasenameNoExtension}.o",
"stopAtEntry": false,
"preLaunchTask": "build"
}
]
}
C. 运行Echo Macros
首先输出一下在build这个task中使用到的宏。
具体来说在运行和调试界面选择配置为Echo Macros

然后按下F5开始运行
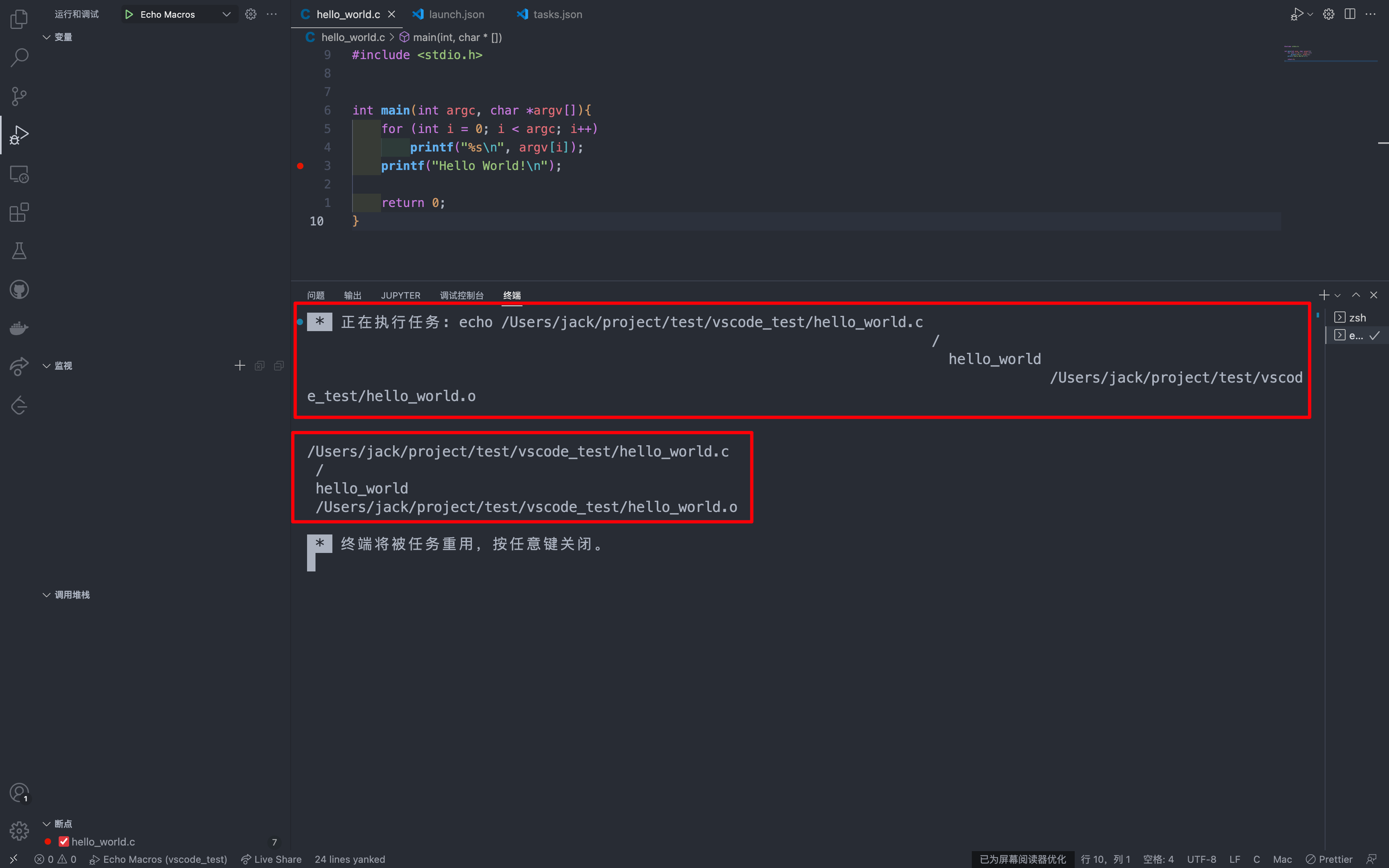
可以看到,上面四个宏的值是
${file} : /Users/jack/project/test/vscode_test/hello_world.c
${pathSeparator} : /
${fileBasenameNoExtension} : hello_world
${fileDirname}${pathSeparator}${fileBasenameNoExtension}.o : /Users/jack/project/test/vscode_test/hello_world.o
D. 运行Gcc Compile
接下来我们运行Gcc Compile,类似的,还是先在运行和调试界面选择Gcc Compile,然后按下F5开始运行
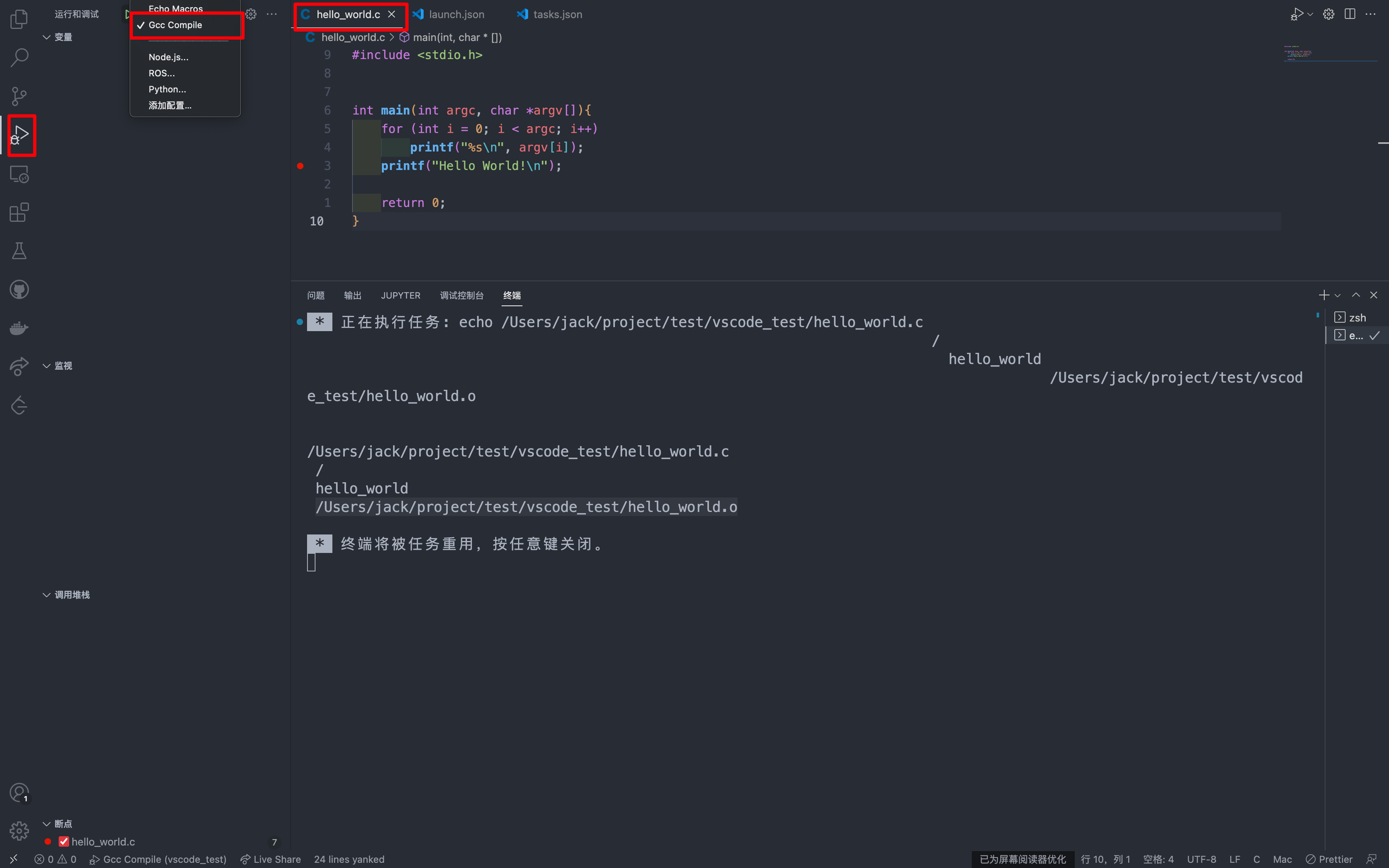
而后我们就会发现在文件夹下就出现了编译后的文件

6. 一个Toy Example:调试程序
我们上面做到了编译程序,而在编译之后我们需要干的就是去调试这个程序。
首先需要明白的是,我们如果想要使用gdb、lldb等调试器去调试一个程序的时候,我们必须要在编译的时候指定-g参数,这样编译器(例如gcc、clang)在编译的时候就会把源代码、符号表等等信息写入到程序里面去。
而后在调试的时候,我们使用命令gdb xxxx/lldb xxxx,gdb/lldb就回去读取源代码和符号表,从而开始调试。
A. tasks.json的内容
我们首先新增加一个名为debug_build的task,具体来说就是在编译的时候加上-g参数
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "debug_build",
"command": "gcc",
"args": [
"${file}",
"-g",
"-o",
"${fileDirname}${pathSeparator}${fileBasenameNoExtension}.o"
]
}
]
}
B. launch.json的内容
为了要进行debug,我们在launch.json中新加入一项,这一项可能会有些复杂
{
// 使用 IntelliSense 了解相关属性。
// 悬停以查看现有属性的描述。
// 欲了解更多信息,请访问: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"name": "LLDB Debug",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}${pathSeparator}${fileBasenameNoExtension}.o",
"stopAtEntry": false,
"preLaunchTask": "debug_build",
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"MIMode": "lldb"
},
]
}
详细的解释如下:
"type":"cppdbg":新加入的这一项的类型是cppdgb,表示C/C++ Debug。因为我们新添加的运行配置的目的就是给C/C++程序Debug,所以我们让这一项的类型是cppdgb。如果我们是别的项目的话,例如是node.js的项目的话,那么我们让这个运行配置的type是node即可"cwd:"${workspaceFolder}":因为在开始调试的时候我们需要在指定的文件夹下运行调试器,所以就需要使用cwd标签指定工作目录,一般制定成项目的根目录,也就是workspaceFolder就行了"MIMode":"lldb":不同的系统上使用的调试器不同,MacOS、Linux、Windows使用的调试器分别是lldb、gdb、msvc/gdb(msvc是Visual Studio带的调试器,gdb是MinGW带的调试器),所以我们需要使用MIMode标签指定使用的调试器的类型。
此外,我们其实还可以使用miDebuggerArgs和miDebuggerPath来专门制定调用调试器时候传入的参数以及调试器的路径。
因为我写这篇博客时候用的是Mac,所以用的调试器就是LLDB
C. 运行LLDB Debug
我们给前面的程序加上一个断点,然后选择运行配置为LLDB Debug,然后按下F5开始调试。

接下来我们就进入了调试页面:
- 下方:显示了所有的任务
- 左侧:显示了当前所有的变量以及变量的值、监视的变量以及表达式、函数的调用堆栈
- 中间:显式了正在调试的程序
- 上方:显式了调试的功能按钮

7. 一个Toy Example:顺序执行
我们上面调试了一个程序。但是在现实中,我们往往在调试前是需要顺序执行多个命令的,而不是简单的编译。
我们接下来给出的Toy Example在启动调试前就将顺序执行两步命令:
- 创建一个
bin文件夹 - 将编译好的源文件输出到
bin文件夹中
A. tasks.json中的内容
我们在tasks.json中创建下面的两个任务
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "create_bin",
"type": "shell",
"command": "mkdir",
"args": [
"-p",
"${workspaceFolder}${pathSeparator}/bin"
]
},
{
"label": "debug_build",
"type": "shell",
"command": "gcc",
"group": "build",
"args": [
"${file}",
"-g",
"-o",
"${fileDirname}${pathSeparator}bin${pathSeparator}${fileBasenameNoExtension}.o"
],
"dependsOn": "create_bin",
},
],
}
create_bin任务就是老三样,没啥好说的。
关键就在于修改之后的debug_build任务,debug_build任务中新增加了一个dependsOn标签,这个标签说明了在运行debug_build任务之前需要运行的任务。
在这里就表示在运行debug_build任务之前,需要运行create_bin任务。
B. launch.json的内容
launch.json中的内容保持不变,还是LLDB Debug
{
// 使用 IntelliSense 了解相关属性。
// 悬停以查看现有属性的描述。
// 欲了解更多信息,请访问: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"name": "LLDB Debug",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}${pathSeparator}bin${pathSeparator}${fileBasenameNoExtension}.o",
"stopAtEntry": false,
"preLaunchTask": "debug_build",
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"MIMode": "lldb",
},
]
}
C. 运行LLDB Debug
运行LLDB Debug的结果如下,可以发现首先bin文件被创建了,接着可执行文件输出到了bin文件夹中,而后开始debug

8. 一个真实的例子:CMake工程
我们上面讲了四个Toy Example,介绍了VSCode的tasks.json和launch.json最基本的功能,接下来我们就把这些功能结合到一起,用VSCode调试一个真实的CMake工程。
A. CMake工程结构及文件
CMake工程的结构如下
tree ./
./
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── main.c
├── wish.c
└── wish.h
0 directories, 4 files
项目的源文件一共有四个,其中:
CMakeLists.txt定义了项目结构wish.c和wish.h定义了libwish静态库main.c调用了libwish库
1 ) CMakeLists.txt
CMakeLists.txt中的内容如下:
project(WISH)
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.9)
set(EXECUTABLE_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/bin)
set(LIBRARY_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/lib)
add_library(
libwish STATIC
wish.c
)
add_executable(
wish
main.c
)
target_link_libraries(wish libwish)
2 ) wish.h 和 wish.c
// wish.h
#ifndef _WISH_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#define _WISH_H 1
#define WISH_EXIT_SUCCESS 0
#define WISH_EXIT_FAILURE -1
#define WISH_BUF_SIZE 1024
#define WISH_MY_SEARCH 1
#define WISH_BUILTIN_NUM sizeof(builtin_str) / sizeof(char *)
#define WISH_MAX_WORD 20
#define WISH_MAX_FNAME 1024
#define WISH_MAX_PATH 128
#define WISH_DEBUG 1
// Base Functions
void wish_loop(void); // main loop of wish
char *wish_read_line(void); // read user input line
char **wish_split_line(char *line); // split user input line into words
int wish_redirection(char *args[]); // parse user input token to
int wish_execute(char *args[], int rarg_sht); // execute user input command
int wish_launch(char *args[], int rarg_sht); // launch other program
char *wish_search(char *cmd); // search program in PATH
void wish_error(); // report error
void wish_line(int);
int wish_cd(char **args);
int wish_exit(char **args);
int wish_path(char **args);
int wish_help(char **args);
int wish_env(char **args);
#endif
// wish.c
#include "wish.h"
// path
char *path[WISH_MAX_PATH] = {
[0] = "/bin"
};
// Shell Builtin Funtions
char *builtin_str[] = {
"cd",
"exit",
"path",
"help",
"wenv"
};
int (*builtin_func[])(char **) = {
&wish_cd,
&wish_exit,
&wish_path,
&wish_help,
&wish_env
};
void wish_loop(void){
char *line;
char **args;
bool status;
do
{
printf("wish> ");
line = wish_read_line();
args = wish_split_line(line);
int i = -1;
if ((i = wish_redirection(args)) != -1){
args[i++] = 0;
}
status = wish_execute(args, i);
free(line);
for (int i = 0; i < WISH_MAX_WORD; i++)
if (NULL != args[i])
free(args[i]);
free(args);
} while (status);
if (!status)
exit(WISH_EXIT_FAILURE);
return;
}
char *wish_read_line(void){
int position = 0;
int bufsize = WISH_BUF_SIZE;
char * buffer = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * bufsize);
if(NULL == buffer){
fprintf(stderr, "wish: Memory allocation failed for read line.\n");
exit(WISH_EXIT_FAILURE);
}
char c;
while (true)
{
// read a char
c = getchar();
if (c == EOF || c == '\n'){
buffer[position++] = '\0';
return buffer;
} else
buffer[position++] = c;
// resize buffer
if (position >= bufsize){
bufsize += WISH_BUF_SIZE;
char * temp = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * bufsize);
if(NULL == temp){
fprintf(stderr, "wish: Memory allocation failed for read line.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// copy and reset pointer to new buffer
int num = position;
while (num > 0){
temp[num] = buffer[num];
num--;
}
free(buffer);
buffer = temp;
}
}
}
char **wish_split_line(char *line){
char **words = (char **) malloc(sizeof(char *) * WISH_MAX_WORD);
for (int i = 0; i < WISH_MAX_WORD; i++)
words[i] = (char *)0;
int j = 0, k = 0;
int len = strlen(line);
char *temp = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * len);
for (int i = 0; i < len + 1; i++){
temp[j] = line[i];
if (temp[j] == ' ' || temp[j] == '\t' || temp[j] == '\0'){
temp[j] = '\0';
words[k] = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * (i + 1));
strncpy(words[k], temp, i);
words[k][i] = '\0';
j = 0, k += 1;
} else
j += 1;
}
free(temp);
return words;
}
int wish_redirection(char **args){
int i = 0;
while (args[i] != 0)
{
if (args[i][0] == '>')
return i;
i += 1;
}
return -1;
}
int wish_execute(char *args[], int rarg_sht){
if (NULL == args[0])
return 1;
// run builtin command
for (int i = 0; i < WISH_BUILTIN_NUM; i++)
if (strcmp(args[0], builtin_str[i]) == 0)
return (*builtin_func[i])(args);
return wish_launch(args, rarg_sht);
}
int wish_launch(char *args[], int rarg_sht){
// search path
int i = 0;
char *executable_path = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * WISH_MAX_FNAME);
for (int j = 0; j < WISH_MAX_FNAME; j++)
executable_path[j] = '\0';
char * temp_path = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * WISH_MAX_FNAME);
while (path[i] != NULL) {
// copy path[i] to temp and then concate
if (strncpy(temp_path, path[i], strlen(path[i])) == NULL){
wish_error();
wish_line(__LINE__);
return WISH_EXIT_FAILURE;
}
int len = strlen(temp_path);
temp_path[len] = '/';
temp_path[len + 1] = '\0';
if (strcat(temp_path, args[0]) == NULL){
wish_error();
wish_line(__LINE__);
return WISH_EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// check privilege
if(access(temp_path, X_OK) == 0){
if (strcpy(executable_path, temp_path) == NULL){
wish_error();
wish_line(__LINE__);
return WISH_EXIT_FAILURE;
}
break;
}
i++;
}
free(temp_path);
// print error if not found
if (executable_path[0] == '\0'){
free(executable_path);
wish_error();
wish_line(__LINE__);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
int status;
pid_t son_pid, wait_pid;
son_pid = fork();
if (son_pid == 0){
// child process
// redirection
if (-1 != rarg_sht && NULL != args[rarg_sht]){
// get real path
char rp[WISH_MAX_FNAME];
realpath(args[rarg_sht], rp);
if (NULL == freopen(rp, "w", stdout))
fprintf(stderr, "wish: redirection file %s open fail!\n", rp);
}
// run cmd
int (*func)();
if (WISH_MY_SEARCH == 1)
func = execvp;
else
func = execv;
if (func(args[0], args) == -1){
// wish_error();
// wish_line(__LINE__);
return 1;
}
// if run the following code, then it is wrong
exit(WISH_EXIT_FAILURE);
} else if (son_pid < 0)
perror("wish: son process create fail by fork");
else {
do {
wait_pid = waitpid(son_pid, &status, WUNTRACED);
} while (!WIFEXITED(status) && !WIFSIGNALED(status));
}
return true;
}
char *wish_search(char *cmd){
return (char *)0;
}
void wish_error(){
char *err_msg = "An error has occurred\n";
write(STDERR_FILENO, err_msg, strlen(err_msg));
}
void wish_line(int lineno){
#ifdef WISH_DEBUG
fprintf(stderr, "in line %d\n", lineno);
#endif
}
int wish_cd(char *args[]){
if (NULL == args[1])
wish_error();
else
if (chdir(args[1]) != 0)
wish_error();
return 1;
}
int wish_exit(char *args[]){
if (NULL == args[1])
exit(0);
wish_error();
return 1;
}
int wish_path(char *args[]){
int i = 0;
while ((path[i] = args[i+1]) != NULL)
i++;
return 1;
}
int wish_env(char *args[]){
if (NULL == args[1])
return 1;
else {
char * env = getenv(args[1]);
printf("%s:\n", args[1]);
printf("%s\n", env);
}
return 1;
}
int wish_help(char *args[]){
printf("WISH written by Shihong Wang.\n");
printf("Usage: command argument [enter]\n");
printf("Builtin commands:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < WISH_BUILTIN_NUM; i++)
printf("\t%s", builtin_str[i]);
printf("\nRefer man page of other command.\n");
return 1;
}
3 ) main.c
#include "wish.h"
extern char **environ;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc == 1)
{
// command loop mode
wish_loop();
}
else
{
// read-parse-execute mode
FILE *file;
if (NULL == (file = fopen(argv[1], "r")))
{
fprintf(stderr, "wish: read-parse mode %s file not exists!\n", argv[1]);
exit(WISH_EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// read a line, parse and execute
int status;
char ** args;
size_t len = 0;
ssize_t read;
char *line = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * WISH_BUF_SIZE);
while ((read = getline(&line, &len, file)) != -1)
{
int j = -1;
while (line[++j] != '\n');
line[j] = '\0';
args = wish_split_line(line);
int i = -1;
if ((i = wish_redirection(args)) != -1){
args[i++] = 0;
}
status = wish_execute(args, i);
for (int i = 0; i < WISH_MAX_WORD; i++)
if (NULL != args[i])
free(args[i]);
free(args);
}
free(line);
}
return WISH_EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
B. tasks.json的内容
我们在调试前,需要:
- 创建
build文件夹 - 进入
build文件夹使用cmake配置项目 - 使用
make或者cmake --build ./ --target all进行编译
因此,我们需要再tasks.json中定义三个任务
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "create_build",
"type": "shell",
"command": "mkdir",
"args": [
"-p",
"${workspaceFolder}/build"
],
"detail": "创建build文件夹",
},
{
"label": "cmake_configure",
"type": "shell",
"command": "cmake",
"options": {
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}/build"
},
"args": [
"-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=${input:CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE}",
"-DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=ON", // 生成compile_commands.json 供c/c++扩展提示使用
"../"
],
"dependsOn": "create_build",
"detail": "CMake配置项目"
},
{
"label": "make_build",
"type": "shell",
"command": "make",
"options": {
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}/build"
},
"args": [
"all"
],
"dependsOn": "cmake_configure",
"detail": "Make构建项目"
}
],
"inputs": [
{
"id": "CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE",
"type": "pickString",
"description": "选择项目的编译类型(CMake Build Type)",
"options": [
"Debug",
"Release",
"RelWithDebInfo",
"MinSizeRel",
],
"default": "Debug"
}
]
}
关于input标签,参考手册的这一节:https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/editor/variables-reference
C. launch.json的内容
launch.json的内容如下
{
// 使用 IntelliSense 了解相关属性。
// 悬停以查看现有属性的描述。
// 欲了解更多信息,请访问: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"name": "LLDB Debug",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/bin/wish",
"stopAtEntry": true,
"preLaunchTask": "make_build",
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"MIMode": "lldb",
},
]
}
D. 开始调试
按下F5开始调试
.gif)
9. CMake工程常用的tasks.json和launch.json
下面给出一个CMake工程常用的tasks.json和launch.json
// tasks.json
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
// 在根文件夹中执行创建文件夹build的命令
// 除windows系统外执行的命令为`mkdir -p build`
// windows系统是在powershell中执行命令`mkdir -Force build`
"label": "build_dir",
"command": "mkdir",
"type": "shell",
"args": [
"-p",
"build"
],
"windows": {
"options": {
"shell": {
"executable": "powershell.exe"
}
},
"args": [
"-Force",
"build"
],
}
},
{
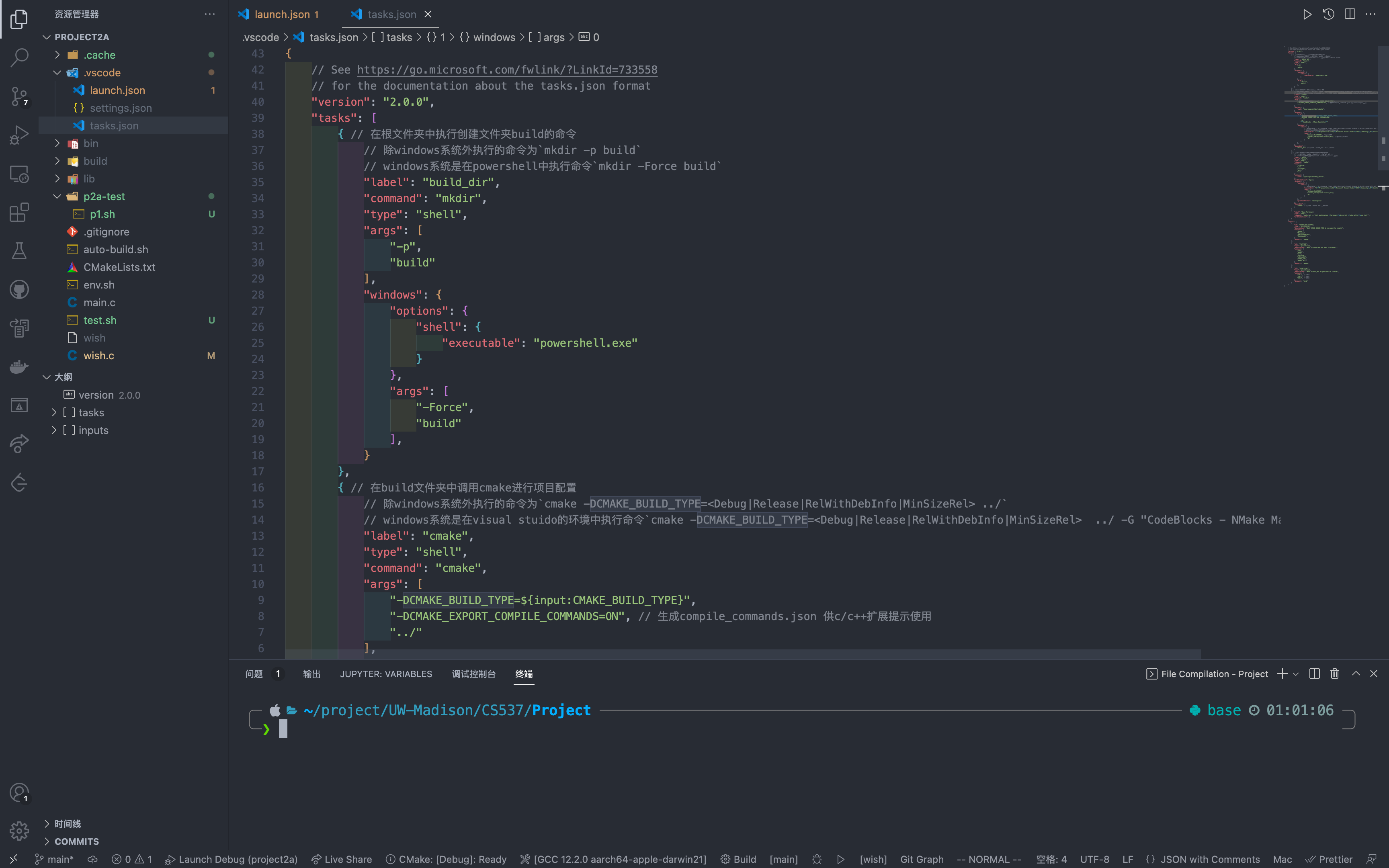
// 在build文件夹中调用cmake进行项目配置
// 除windows系统外执行的命令为`cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=<Debug|Release|RelWithDebInfo|MinSizeRel> ../`
// windows系统是在visual stuido的环境中执行命令`cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=<Debug|Release|RelWithDebInfo|MinSizeRel> ../ -G "CodeBlocks - NMake Makefiles"`
"label": "cmake",
"type": "shell",
"command": "cmake",
"args": [
"-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=${input:CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE}",
"-DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=ON", // 生成compile_commands.json 供c/c++扩展提示使用
"../"
],
"options": {
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}/build",
},
"windows": {
"args": [
"-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=${input:CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE}",
"-DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=ON",
"../",
"-G",
"\"CodeBlocks - NMake Makefiles\""
],
"options": {
"shell": {
// 需要根据安装的vs版本调用vs工具命令提示符,根据自己的计算机上的路径进行修改
"executable": "C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Microsoft Visual Studio\\2019\\Community\\VC\\Auxiliary\\Build\\vcvarsall.bat",
"args": [
"${input:PLATFORM}", //指定平台
"-vcvars_ver=${input:vcvars_ver}", //指定vc环境版本
"&&"
]
}
},
},
"dependsOn": [
"build_dir" // 在task `build_dir` 后执行该task
]
},
{
// 在build文件夹中调用cmake编译构建debug程序
// 执行的命令为`cmake --build ./ --target all --`
// windows系统如上需要在visual stuido的环境中执行命令
"label": "build",
"group": "build",
"type": "shell",
"command": "cmake",
"args": [
"--build",
"./",
"--target",
"all",
"--"
],
"options": {
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}/build",
},
"problemMatcher": "$gcc",
"windows": {
"options": {
"shell": {
"executable": "C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Microsoft Visual Studio\\2019\\Community\\VC\\Auxiliary\\Build\\vcvarsall.bat",
"args": [
"${input:PLATFORM}",
"-vcvars_ver=${input:vcvars_ver}",
"&&"
]
}
},
"problemMatcher": "$msCompile"
},
"dependsOn": [
"cmake" // 在task `cmake` 后执行该task
]
},
{
"label": "Open Terminal",
"type": "shell",
"command": "osascript -e 'tell application \"Terminal\"\ndo script \"echo hello\"\nend tell'",
"problemMatcher": []
}
],
"inputs": [
{
"id": "CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE",
"type": "pickString",
"description": "指定 CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE 的值",
"options": [
"Debug",
"Release",
"RelWithDebInfo",
"MinSizeRel",
],
"default": "Debug"
},
{
"id": "PLATFORM",
"type": "pickString",
"description": "指定 PLATFORM 的值",
"options": [
"x86",
"amd64",
"arm",
"x86_arm",
"x86_amd64",
"amd64_x86",
"amd64_arm",
],
"default": "amd64"
},
{
"id": "vcvars_ver",
"type": "pickString",
"description": "指定 vcvars_ver 的值",
"options": [
"14.2", // 2019
"14.1", // 2017
"14.0", // 2015
],
"default": "14.2"
}
]
}
注意,如果是需要以Attach Debug方式启动的调试的话,运行中的进程在编译的时候必须要加上-g以将符号表写入到程序中,从而能够debug程序,若使用CMake工具的话,需要指定使用Debug方式来构建程序,而非MinSizeRel等其他构建方式
// launch.json
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
//名称
"name": "Launch Debug",
//调试类型,除使用msvc进行调试外,均为该类型
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
//指定C/C++程序位置
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/bin/${input:executable}",
//指定运行参数
"args": [
"test.bin",
"sorted.bin"
],
"stopAtEntry": false,
//指定工作目录
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
//在调试前会先调用build_debug这个task编译构建程序
"preLaunchTask": "build",
"environment": [],
//macOS的特定配置
"osx": {
//指定使用lldb进行调试
"MIMode": "lldb",
// 使用外部终端
"externalConsole": true,
},
//linux的特定配置
"linux": {
//指定使用gdb调试
"MIMode": "gdb",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
]
},
//windows的特定配置
"windows": {
//指定使用msvc进行调试
"type": "cppdbg",
//指定C/C++程序位置
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/build/${workspaceFolderBasename}.exe",
}
},
{
//名称
"name": "Attach Debug",
//调试类型,除使用msvc进行调试外,均为该类型
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "attach",
//指定C/C++程序位置
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/bin/${input:executable}",
//指定要attach的线程
"processId":"${command:pickProcess}",
"osx": {
//指定使用lldb进行调试
"MIMode": "lldb",
// 使用外部终端
"externalConsole": true,
},
//linux的特定配置
"linux": {
//指定使用gdb调试
"MIMode": "gdb",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
]
},
//windows的特定配置
"windows": {
//指定使用msvc进行调试
"type": "cppdbg",
//指定C/C++程序位置
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/build/${workspaceFolderBasename}.exe",
}
}
],
"inputs": [
{
"id": "executable",
"type": "pickString",
"description": "可执行文件的名称",
"default": "posrt",
"options": [
"psort"
]
}
]
}



