本文主要提供了Python版本的哈夫曼压缩算法实现,并在此基础上提供了命令行和基于Qt的GUI用户界面(User Interface)

哈夫曼(Huffman Encoding)压缩算法-Python实现
哈夫曼编码作为计算机届非常底层的算法,不少领域都会出现该算法的身影,例如在MPEG图片压缩算法中等等。因此掌握哈夫曼算法以及相关的哈弗曼编码、哈弗曼树实现还是比较必要的。
0. 前言
我目前是一个大二的计算机系学生,最近数据结构课程的配套实验要求学生从十四个题中选择四个来做。刚好最近学习了PyQt的相关内容,于是本着学习的目的把我完成的成果记录下来,希望我的这篇博客能够帮助大家学习与理解。

1. 编码
所有的文件,包括MP3音频、MP4视频、PDF文档、乃至于可执行文件(Windows上的.EXE、Linux中的.O等ELF格式文件),对于计算机来说都是二进制数据流,即由0101的比特构成的流(Stream)。
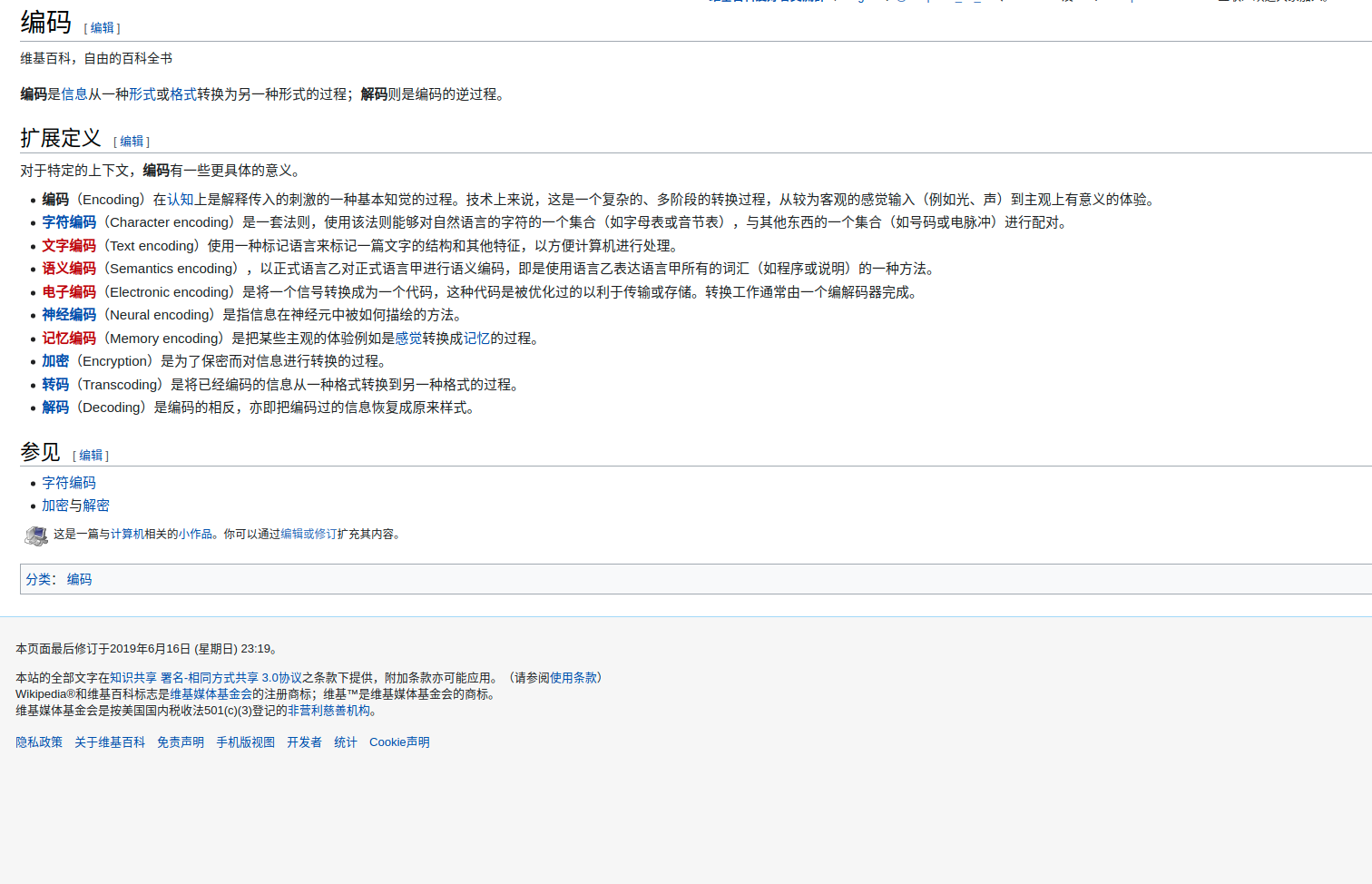
然而二进制流对于计算机而言是有意义的,对人而言却没有多大的意义了,因为人看不懂二进制的字节流。于是为了解决这个问题,就出现了编码。所谓编码即指将信息从一种格式转换为另外一种格式而不改变其内容,更详细的介绍,参考下面百度百科和维基百科的介绍。
From Wikipedia
编码是信息从一种形式或格式转换为另一种形式的过程;解码则是编码的逆过程。
From BaiduBaike:
编码是信息从一种形式或格式转换为另一种形式的过程,也称为计算机编程语言的代码简称编码。用预先规定的方法将文字、数字或其它对象编成数码,或将信息、数据转换成规定的电脉冲信号。编码在电子计算机、电视、遥控和通讯等方面广泛使用。编码是信息从一种形式或格式转换为另一种形式的过程。解码,是编码的逆过程。
因此,编码其实指的就是转变信息的形式而不改变信息的内容。之所以要进行编码与解码,就是因为对于不同的主体而言,不同编码方式的信息的阅读难度和理解难度不同。例如上面的三国演义,对于我们人而言,文字形式的三国演义易于理解而二进制形式的三国演义更利于计算机理解。
换个角度,其实语种之间的转换也是一种编码的转换。例如英语对于中文母语的人就不好理解。而翻译也是把信息从一种语言转换为另一种语言,其形式在变,但本质内涵的信息却没有变。所以究其根本,编码的目的在于方便信息的理解。

话说回来,要进行编码,就需要一张编码表。例如学C语言时候的ASCII表。我们通过编码表构建了两种不同编码之间的映射关系,因此单纯的ASCII字符的转换,就是数值的映射关系,从而通过数值-字符的转换,实现了编码与解码。其实从语言的角度来看,语言的编码不仅仅是单词的映射,还涉及语法的转换等等更加复杂的关系。
然而单纯的使用ASCII编码或者UTF8这种编码方式其实虽然很不错,计算机能够理解,但是他们的问题就是太浪费空间了。例如针对ASCII编码,每一个字符需要8个比特位(0-255)。因此哈夫曼编码除了方便计算机理解以外,更大的好处是能够节约空间。
说了这么久,总算是说到了哈夫曼编码,哈夫曼编码其实就是一种编码,和ASCII编码在本质上没有区别的。
2. 哈夫曼算法 / Huffman Coding
关于哈夫曼编码和对应的哈夫曼算法就不赘述了,在数据结构的课本上其实讲得非常好也非常的透彻。下面就放一下百度百科和维基百科的介绍
From Wikipedia:
霍夫曼编码(英语:Huffman Coding),又译为哈夫曼编码、赫夫曼编码,是一种用于无损数据压缩的熵编码(权编码)算法。由美国计算机科学家大卫·霍夫曼(David Albert Huffman)在1952年发明。
From BaiduBaike:
哈夫曼编码(Huffman Coding),又称霍夫曼编码,是一种编码方式,哈夫曼编码是可变字长编码(VLC)的一种。Huffman于1952年提出一种编码方法,该方法完全依据字符出现概率来构造异字头的平均长度最短的码字,有时称之为最佳编码,一般就叫做Huffman编码(有时也称为霍夫曼编码)。
3. 实现思路
针对不同的功能,整个程序的实现,主要分为三个层面:
- 核心层:负责哈夫曼算法的实现
- 数据存取层:负责任意形式数据的读取、保存
- 用户界面层:负责提供命令行用户界面以及图形用户接口,从而实现
高级感(逼格)
A. 核心层
核心层的任务其实就是构建哈弗曼树、得到哈夫曼编码即可,主要算法其实在数据结构课本、B站视频、知乎上都有不少介绍。
然而一个重要的问题就是课本上和B站中的不少介绍视频都是针对字符(字母)进行哈夫曼编码的。我们由于要对任意格式的文件进行编码,因此就要从数据的本源:字节,进行哈夫曼编码。因此我们哈弗曼树的叶子节点实际上是字节。我们以8位二进制作为一个单元(Symbol)。然后针对这个Symbol进行编码。因此我们编码的对象就从26个字母变成了256种八位二进制数字。换而言之我们是对0~255这256个数字进行编码。
然后根据得到的哈夫曼编码将原字节数据一个字节(八位比特)进行编码、转换为哈夫曼编码即可。
B. 数据存取层
在数据存取层,我们假设现在已经对原数据(raw data)构建出了哈弗曼树并且得到了原数据的哈弗曼编码,而且根据这些哈夫曼编码得到了原数据的哈夫曼编码字节流。我们在数据存取层需要做的就是
- 保存转换后的新的哈夫曼编码的字节流
- 读取原始数据的二进制字节流
- 保存哈夫曼编码表
读取原始数据的二进制字节流其实问题不大,Python中以rb(read byte)模式打开文件即可。而哈夫曼编码表的保存则可以利用Python的Pickle模块将Python中的对象保存到磁盘/从磁盘中加载(我们以字典/映射的形式保存编码表)
因此数据存取层的关键就在于如何保存编码后的哈夫曼编码字节流?这个问题看似简单,其实有一个问题,就是(二进制)数据在计算机外存(固态、硬盘)中的保存都是整字节整字节的保存的,读取也是整字节整字节读取的。而我们对原文件的二进制流进行哈夫曼编码后实际上其长度是不定的,不一定是整字节的。
因此保存的时候虽然我们可以强行以整字节整字节的保存编码后的二进制流,但是在最后一位由于不一定是一个整字节,因此实际上存在问题。为了处理这个问题,我们设定一个特殊的字符EOF,由于8位二进制能表示256个数字(Symbol),而这些数字都有可能出现在原字节流中,因此我们是不能直接选取一个数字来表示文件结尾的。为此,在Python中,通过一个特定的类来实现文件结尾的表示,即我们自定义的EOF。在大文件(几MB的文件)中,一共有1024*1024个字节,因此从0~255这256个数字出现的次数一定是远远大于1的,而EOF的出现次数永远为1,因此必然会拥有最长的编码。
在我们转换完所有的原数据之后,我们把EOF添加到末尾去,并且如果最后不满足8位的话在最后补0。而在读取的时候,我们只需要获取最长长度的编码的长度,然后对最后一个字节做截取即可得到正确的完整的带有EOF的编码的编码后的原数据的哈夫曼编码字节流。
C. 用户界面层
在用户界面层,不关心具体的哈夫曼编码的实现、数据的保存方式等这些具体的细节。相比,用户界面层仅关注如何提供一个用户友好的用户界面。例如在终端(Terminal)提供选项,让用户制定压缩、解压的文件。还会检查用户指定的文件是否存在、查找用户需要解码的文件对应的的哈弗曼编码表的文件位置。
当然,GUI使用会让程序显得非常高级,因此GUI部分是必须的。而完成GUI程序,则借助Qt来完成,即使用Qt的Python Binding。
当然,为了便于写代码管理与开发,需要注意GUI的代码要与完成功能的代码在逻辑和形式上分离,因此采取前面所说的分层的思想。
因此将GUI作为用户界面层的一个组件(另一个组件为终端命令行接口),调用由数据存取层提供的接口函数完成功能。
在GUI内部,进行在GUI窗口上发生的事件的监听,以及轮转调度、回调函数调用等等功能。
4. 具体代码
本部分根据上面的讲解,对照代码进行详细的介绍。
项目结构如下
(base) jack@Alienware:~/projects/data_structure/11_huffman$ tree -L 2
.
├── ErrorHuffman.py
├── huff.py
├── resources
│ ├── 三国演绎.txt
│ ├── D_Star_illustration.pptx
│ ├── ICRA2022.pdf
│ ├── romance_of_three_kingdoms.rar
│ ├── Song.mp3
│ ├── str.txt
│ └── test.mp4
├── ui
│ └── main.ui
└── Ui_main.py
2 directories, 11 files
其中:
- resource为项目资源文件夹,主要存放稍后用于验证压缩的资源,包括MP4、txt、MP3、rar、PDF等多种格式文件
- ui为程序图形界面配置文件,负责设定界面大小、按钮位置等配置参数。而UI_main为具体的按钮等控件的实现代码
- huff.py为最终的程序,内含所有完整代码;errHuff.py为先前写错的代码,问题出在了哈夫曼建树的时候得到的不是范式哈弗曼树,因此该程序遍历哈弗树得到哈夫曼编码的时候有问题,最后压缩出来的文件比源文件大了好几倍(反向压缩。。。应了刘某的反向抽烟XXX😂)
1. 导入库
主要导入的库为命令行参数获取库argparse、Python对象序列化库Pickle、路径处理库pathlib、堆管理库heapq、GUI库PyQt以及为了更好的显示得到的哈夫曼编码表的pandas库与命令行彩色输出的colorama库。
最后定义了文件的私有变量设定作者和日期,以及将可能存在源代码的文件加入文件搜索路径(类似于Linux环境变量LD_LIBRARY_PATH)
import sys
import pickle
import argparse
import itertools
import collections
from pathlib import Path
from heapq import heapify, heappush, heappop
from typing import Union, Any, Dict, List, Tuple
from PyQt5.QtCore import QDir
import pandas
import pandas as pd
from colorama import Fore, Style
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
__author__ = "Jack Wang"
__date__ = "2021/12/19"
sys.path.append(Path(__file__).resolve().parent.joinpath("./ui").__str__())
2. 定义EOF符号
EOF符号由于和0-255个数字一样将在构建树的进行比较,因此需要重载如等于(__eq__)、大于(__gt__)、小于(__lt__)等运算符。在Python中重载运算符以魔术方法(double underline)实现。最后由于在序列化以及字典中保存符号-哈夫曼编码键值对的时候,符号作为字典的键需要时可哈希的对象(Hashable),因此重写__hash__方法,以实现作为字典的键。
注意,上面说过了EOF需要保证编码是最长的,因此当合别人比大的时候总是False,比小的时候总是True,并且只会等于同样是EOF的对象
class _EOFSymbol:
"""
Notes:
_EOFSymbol 是内置的文件结尾的类,用于在编码的时候标志文件的结尾。
由于在进行哈夫曼树的构建的时候需要选出来权最小的节点,因此需要重写比较的魔术方法。
默认文档结尾是频率最少的字符,因此和任何数字比较
"""
def __repr__(self):
return "_EOF"
def __lt__(self, other):
return True
def __gt__(self, other):
return False
def __eq__(self, other):
return self.__class__ == other.__class__
def __hash__(self):
return hash(self.__class__)
_EOF = _EOFSymbol()
3. 哈夫曼编码
采用工厂模式,实现哈夫曼编码与解码的核心对象为_HuffmanCoder,与用于构建_HuffmanCoder的HuffmanFactory类。
_HuffmanCoder类负责:
- 输出/打印哈夫曼编码表:get_code_table方法、print_code_table方法
- 编码、解码字节流序列:_encode_streaming方法、_decode_streaming方法
- 为用户界面层提供统一接口:encode方法、decode方法
- 保存、加载哈夫曼编码表:save方法、load方法
其初始化参数负责接受已经获得的编码表和符号的拼接方式以及eof符号定义
此外save方法通过Python内建的字典将类的元数据保存到字典中,并利用Python的Pickle模块序列化到磁盘上。而load方法则通过类方法,在通过Pickle加载通过save方法保存到磁盘上的数据后显示调用类的初始化方法以实现_HuffmanCoder类的重构。
此外,在保存的时候需要确保保存的文件的路径存在,因此编写ensure_dir函数,而_guess_concat_function则是为支持多种类型的Symbol(字符串、二进制流(串))在编码、解码时候拼接所写的函数,即根据输入的类型来获得拼接方法的函数。
HuffmanCoderFactory类负责:
- 获得哈夫曼编码表:from_frequencies方法
- 创建_HuffmanCoder类:from_sequence方法、from_frequencies方法。
其中from_frequencies接受符号-频数键值对并构建哈弗曼树、获得哈夫曼编码表;from_sequence负责统计序列中的符号的频数,由于需要对任意的数据进行压缩,因此符号即指一个字节。
在进行构建的时候,利用优先队列,以出现频率作为优先级进行排列,每次pop都会获得优先队列顶的元素,即出现频率最小的元素。
而队列中的每个元素,则是一个元组,元祖的第一个元素为权值(频率),第二个元素为以该节点为祖宗的叶子节点的二进制编码(以数字形式表现)和对应的比特位数(所处的哈弗曼树的层数/深度)对。使用数字是由于位移操作方便构建哈弗曼编码而记录比特位数则是为了记录开头为0的哈夫曼编码的总位数。
具体流程为只要队列(森林)中的节点多于1个,则首先弹出权值较小的子树a与权值较大的子树b,将子树a与b的频率相加作为新的子树的频率,而后将子树a的所有的叶子节点的深度+1(比特位数),然后在原二进制编码前加上0(维持不变)。而对子树b,将其所有的叶子节点的二进制编码前加上1(将1左移原有比特位数(原有深度),然后加上当前二进制编码),最后将其深度(比特位数)加1。即使用递归的方式完成哈弗曼树的构建与哈夫曼编码的同步获取。
def _guess_concat_function(data):
"""
Notes:
To support multiple types of input, e.g., str, bytes, list, there must be a
function that return the needed concat function
Returns:
pass
"""
return {type(u""): u"".join, type(b""): bytes}.get(type(data), list)
def ensure_dir(path: Union[str, Path]) -> Path:
path: Path = path if isinstance(path, Path) else Path(path)
if not path.exists():
path.mkdir(parents=True)
assert path.is_dir()
return path
class _HuffmanCoder:
"""
Notes:
_HuffmanCoder, which provide encode, decode, serialize, deserialize, save_code, load_code functionalities.
Args:
"""
def __init__(self, code_table: Dict[Any, Tuple[int, int]], concat=list, check=True, eof=_EOF):
"""
Notes:
initialize method of _HuffmanCoder with given code table
Args:
code_table (Dict[Any, Tuple[int, int]]): code table of all symbols in the encoding sequence, create automatically by
HuffmanCoderFactory, items are Tuple[Symbol, [depth, bit]]
concat: concat method of symbols, will be automatically determined in HuffmanCoderFactory
check: valid code table's format
eof: eof symbol, leave it alone
"""
self._table = code_table
self._concat = concat
self._eof = eof
if check:
assert isinstance(self._table, dict), f"{Fore.RED}Code table need to be a dict!{Style.RESET_ALL}"
assert all(
isinstance(b, int) and b >= 1 and isinstance(v, int) and v >= 0 for (b, v) in self._table.values()
), f"{Fore.RED}Code table internal format Error!{Style.RESET_ALL}"
def get_code_table(self) -> Dict[Any, Tuple[int, int]]:
"""
Notes:
get_code_table returns code table of input sequence
Returns:
self._table
"""
return self._table
def print_code_table(self, verbose=False) -> pandas.DataFrame:
"""
Notes:
print_code_table is used to print code table
Args:
verbose (bool): if True, then print the table in a pretty format
Returns:
pd.DataFrame
"""
pd.options.display.max_rows = None
columns = list(zip(*list(zip(*itertools.chain(
[("Symbol", "Huff Code", "BitSize")], (
(repr(symbol), bin(val)[2:].rjust(bits, "0"), str(bits))
for symbol, (bits, val) in self._table.items()
)
)))))
df = pd.DataFrame(columns[1:], columns=columns[0])
if verbose:
print(df)
return df
def _encode_streaming(self, raw_sequence):
size = 0
buffer = 0
for s in raw_sequence:
bits, values = self._table[s]
buffer = (buffer << bits) + values
size += bits
while size >= 8:
byte = buffer >> (size - 8)
yield byte
buffer = buffer - (byte << (size - 8))
size -= 8
if size > 0:
bit, value = self._table[self._eof]
buffer = (buffer << bit) + value
size += bit
if size > 8:
byte = buffer >> (size - 8)
else:
byte = buffer << (8 - size)
yield byte
def _decode_streaming(self, encoded_sequence):
# Reverse lookup table: map (bitsize, value) to symbols
lookup = {(b, v): s for s, (b, v) in self._table.items()}
buffer = 0
size = 0
for byte in encoded_sequence:
for m in [128, 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1]:
buffer = (buffer << 1) + bool(byte & m)
size += 1
if (size, buffer) in lookup:
symbol = lookup[size, buffer]
if symbol == self._eof:
return
yield symbol
buffer = 0
size = 0
def encode(self, raw_seq):
"""
Notes:
encode is used to encode the sequence that build the huffman tree
Args:
raw_seq: sequence that build the huffman tree
Returns:
bytes
"""
return bytes(self._encode_streaming(raw_seq))
def decode(self, encoded_seq, concat=None):
return (concat or self._concat)(self._decode_streaming(encoded_seq))
def save(self, path: Union[str, Path], metadata: Any = None):
code_table = self.get_code_table()
data = {
"code_table": code_table,
"type": type(self),
"concat": self._concat,
}
if metadata:
data['metadata'] = metadata
path = Path(path)
ensure_dir(path.parent)
with path.open(mode='wb') as f:
pickle.dump(data, file=f)
@staticmethod
def load(path: Union[str, Path]) -> '_HuffmanCoder':
path = Path(path)
with path.open(mode='rb') as f:
data = pickle.load(f)
cls = data['type']
assert issubclass(cls, _HuffmanCoder)
code_table = data['code_table']
return cls(code_table, concat=data['concat'])
class HuffmanCoderFactory(_HuffmanCoder):
"""
Notes:
HuffmanCodecFactory is the class that create HuffmanCoder from different type of inputs
Methods:
from_frequencies: create HuffmanCoder from frequency table
"""
@classmethod
def from_frequencies(cls, frequencies: Dict[Any, int], concat=None, eof=_EOF):
"""
Notes:
from_frequencies creates huffman codec by symbol-frequency table/mapping.
Args:
frequencies (Dict[Any, int]): Symbols and its frequency, symbols can be str, bytes or int, etc.
concat (Union[None]): concat method of symbols, will be determined by the function if argument is not
specified
eof (_EOFSymbol): leave it alone.
Returns:
__HuffmanCoder
Examples:
>>> huf_coder = HuffmanCoderFactory.from_frequencies({"a":29, "b":10, "c": 5})
>>> type(huf_coder)
"""
concat_function = concat if concat is not None else _guess_concat_function(next(iter(frequencies)))
# build huffman tree node heap
# each item: (frequency, [(symbol, (bitsize, value))], value equals which layer of the tree
heap: List[Tuple[int, List[Tuple[Any, Tuple[int, int]]]]] = [(freq, [(symbol, (0, 0))]) for symbol, freq in
frequencies.items()]
# add eof
if eof not in frequencies:
heap.append((1, [(eof, (0, 0))]))
heapify(heap)
while len(heap) > 1:
# get first 2 min as left and right child tree
a: Tuple[int, List[Tuple[Any, Tuple[int, int]]]] = heappop(heap)
b: Tuple[int, List[Tuple[Any, Tuple[int, int]]]] = heappop(heap)
# merge child to form parent
# parent frequencies adds together, left child add 0 ahead (do nothing) of previous bits
# right add 1 ahead of previous bits
merged = (
a[0] + b[0],
[(s, (n + 1, v)) for (s, (n, v)) in a[1]] + [(s, (n + 1, (1 << n) + v)) for (s, (n, v)) in b[1]]
)
heappush(heap, merged)
# code table is root
table = dict(heappop(heap)[1])
return cls(table, concat=concat, check=False, eof=eof)
@classmethod
def from_sequence(cls, sequence: Union[List[Any], Tuple[Any], str, bytes]):
"""
Notes:
from_sequence will build a huffman tree from a sequence of symbol
Args:
sequence (Union[List, Tuple][Any]):
Returns:
__HuffmanCoder
Examples:
>>> seq = "a"*100 + "b"*29 + "c"*32
>>> coder = HuffmanCoderFactory.from_sequence(seq)
"""
frequencies = collections.Counter(sequence)
return cls.from_frequencies(frequencies, concat=_guess_concat_function(sequence))
4. 哈夫曼编码层接口
为实现GUI与哈弗曼编码解耦,在前面哈夫曼编码的核心类的基础上,编写哈弗曼编码接口函数,完成编码、解码一步到位
其中:
- encode负责读取文件的二进制流、压缩、输出压缩时的摘要信息
- decode负责读取文件的二进制流、解压、输出解压时的摘要信息
def encode(path: Union[str, Path], verbose: bool=True):
assert (path := Path(path)).exists(), f"{Fore.RED}{path} not exists!{Style.RESET_ALL}"
with path.open(mode="rb") as f:
content = f.read()
coder = HuffmanCoderFactory.from_sequence(content)
byte = coder.encode(content)
if not (out_fd := path.resolve().parent / (path.stem + "_huf")).exists():
out_fd.mkdir(parents=True)
with (main_path := out_fd.joinpath(path.stem + "_" + path.suffix[1:] + ".huf")).open("wb") as f:
f.write(byte)
coder.save(coder_path := out_fd.joinpath(path.stem + "_coder.huf"))
b1 = path.stat().st_size
b2 = main_path.stat().st_size
b3 = coder_path.stat().st_size
summary1, summary2, summary3, summary4 = [""]*4
if verbose:
summary1 = f"Origin file: {path.stem}{path.suffix}, byte size: {b1}"
summary2 = f"Compressed file: {main_path.stem}{main_path.suffix}, byte size: {b2}"
summary3 = f"HuffCoder file: {coder_path.stem}{coder_path.suffix}, byte size: {b3}"
summary4 = f"{Fore.GREEN}Compression rate {b2}/{b1}={Style.BRIGHT}{round(b2/b1, 4)*100}%{Style.NORMAL}" +\
f", saved {Style.BRIGHT}{b1-b2}{Style.RESET_ALL} bytes"
print(s := "Summary".center(max([len(summary1), len(summary2), len(summary3), len(summary4)]), "="))
print("\n".join((summary1, summary2, summary3, summary4)))
print("="*len(s))
return b1, b2, b3, coder
def decode(huf_path: Union[Path, str], coder_path: Union[Path, str], verbose: bool=True):
huf_path, coder_path = Path(huf_path), Path(coder_path)
coder = _HuffmanCoder.load(coder_path)
with huf_path.open(mode="rb") as f:
content = f.read()
decoded = coder.decode(content)
with (dec_path := huf_path.parent.joinpath((s := huf_path.stem.split("_"))[0] + f"_decode.{s[1]}")).open(mode="wb") as f:
f.write(decoded)
b1 = huf_path.stat().st_size
b2 = coder_path.stat().st_size
b3 = dec_path.stat().st_size
if verbose:
summary1 = f"Origin file: {huf_path.stem}{huf_path.suffix}, byte size: {b1}"
summary2 = f"Coder file: {coder_path.stem}{coder_path.suffix}, byte size: {b2}"
summary3 = f"Decompressed file: {dec_path.stem}{dec_path.suffix}, byte size: {b3}"
summary4 = f"{Fore.GREEN}Decompression rate {b3}/{b1}={Style.BRIGHT}{round(b3/b1, 4)*100}%{Style.NORMAL}" +\
f", lost {Style.BRIGHT}{b3-b1}{Style.RESET_ALL} bytes"
print(s := "Summary".center(max([len(summary1), len(summary2), len(summary3), len(summary4)]), "="))
print("\n".join((summary1, summary2, summary3, summary4)))
print("="*len(s))
return b1, b2, b3, coder
5. 用户接口层
用户接口层负责提供命令行用户界面以及GUI用户界面
A. GUI用户界面
GUI用户界面由于会接管程序流的控制,因此以类的形式进行封装。
其中:
- initUI方法负责窗口的UI设计、按钮等控件的信号对应的槽函数(信号处理函数)的绑定
- fileDialog方法负责暂时接管程序流,以GUI的形式帮助用户进行文件的选择,以Dialog的形式暂时接管程序运行
- compress方法作为压缩按钮的槽函数,负责文件的压缩,在进行文件路径检查(文件存在)之后,调用哈夫曼编码层提供的接口函数进行压缩,并将摘要信息输出到程序显示框内
- decompress方法作为解压按钮的槽函数,负责文件的解压,在进行文件路径检查(压缩文件以及哈夫曼编码表文件均存在)之后,调用哈夫曼编码层提供的接口函数进行解压,并将摘要信息输出到程序显示框内
class QtGUIHuff(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
from Ui_main import Ui_Form
self.ui = Ui_Form()
self.ui.setupUi(self)
self.setWindowTitle("哈夫曼压缩/解压缩程序")
self.ui.compress.clicked.connect(self.compress)
self.ui.decompress.clicked.connect(self.decompress)
def fileDialog(self):
dialog = QFileDialog()
dialog.setFileMode(QFileDialog.AnyFile)
dialog.setFilter(QDir.Files)
if dialog.exec():
filename = dialog.selectedFiles()
return Path(filename[0])
else:
return False
def compress(self):
f_path = self.fileDialog()
self.ui.textEdit.setReadOnly(True)
s = ["开始压缩"]
self.ui.textEdit.setText("\n".join(s))
result = encode(f_path)
summary1 = f"Origin file: {f_path.stem}{f_path.suffix}, byte size: {result[0]}"
summary2 = f"Compressed file: byte size: {result[1]}"
summary3 = f"HuffCoder file: , byte size: {result[2]}"
summary4 = f"Compression rate {result[1]}/{result[0]}={round(result[1]/result[0], 4)*100}%" + \
f", saved {result[0] - result[1]} bytes"
self.ui.textEdit.setText("\n".join([*s, summary1, summary2, summary3, summary4, "压缩结束"]))
self.ui.textEdit_2.setText(result[-1].print_code_table(verbose=False).__str__())
def decompress(self):
f_path = self.fileDialog()
if f_path.suffix != ".huf":
QMessageBox.warning(self, "警告", "请选择正确的压缩文件路径", QMessageBox.Yes, QMessageBox.Yes)
return False
if len(ps := list(Path(f_path).parent.glob("*.huf"))) == 2:
print(ps)
for p_idx in range(len(ps)):
if "coder" in ps[p_idx].stem:
cp_idx = p_idx
else:
QMessageBox.warning(self, "警告", "缺少必要的解压缩文件", QMessageBox.Yes, QMessageBox.Yes)
return False
s = ["开始解压"]
import time
time.sleep(1)
self.ui.textEdit.setText("\n".join(s))
result = decode(huf_path:=ps[1-cp_idx], coder_path:=ps[cp_idx])
summary1 = f"Origin file: {huf_path.stem}{huf_path.suffix}, byte size: {result[0]}"
summary2 = f"Coder file: {coder_path.stem}{coder_path.suffix}, byte size: {result[1]}"
summary3 = f"Decompressed file: byte size: {result[2]}"
summary4 = f"Decompression rate {result[2]}/{result[0]}={round(result[2]/result[0], 4)*100}%" +\
f", lost {result[2] - result[0]} bytes"
self.ui.textEdit.setText("\n".join([*s, summary1, summary2, summary3, summary4, "解压结束"]))
self.ui.textEdit_2.setText(result[-1].print_code_table(verbose=False).__str__())
B. Terminal用户界面
Terminal用户界面则是以argparse库中的ArgumentParser对象完成命令行参数的接受,稍后在主程序中配合完成用户界面。设定了-h参数输出帮助信息、-s对指定路径的文件进行压缩、-t对指定路径的文件进行解压、-g以GUI用户界面运行程序,-v将压缩/解压摘要输出到命令行窗口
def parse_args() -> argparse.Namespace:
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description="哈夫曼压缩算法Python实现,可以对任意文件进行压缩,提供命令行以及GUI用户界面。作者:Jack Wang"
)
parser.add_argument("-s", "--src", dest="src_path", type=str, default=None, help="需要压缩的文件路径")
parser.add_argument("-t", "--target", dest="target_path", type=str, default=None, help="需要解压文件所在的文件夹的路径")
parser.add_argument("-v", "--verbose", dest="v", action="store_true", help="是否显示压缩的摘要信息")
parser.add_argument("-g", "--gui", dest="gui", action="store_true", help="是否以GUI方式显示")
return parser.parse_args()
6. 主程序
主程序很简单,根据接受的命令行参数调用不同的接口即可
在非图形界面的运行的时候,程序的主控制流以程序为主,而以GUI方式运行的时候,程序的控制流则在Qt框架下,用户级线程调度、事件监听、信号分发、槽函数(信号处理函数)唤醒等均由框架负责。
def main(args: argparse.Namespace):
if not args.gui:
assert 0 < int(args.src_path is not None) + int(args.target_path is not None), f"{Fore.RED}请选择压缩或者解压,使用-h查询用法{Style.RESET_ALL}"
if not args.gui:
print(f"{Fore.GREEN}命令行工作模式{Style.RESET_ALL}")
if args.src_path is not None:
print(f"开始压缩 {args.src_path}")
if args.v:
print(encode(Path(args.src_path))[-1].print_code_table(verbose=False))
else:
encode(Path(args.src_path), verbose=False)
print("压缩完成")
elif args.target_path is not None:
if len(ps := list(Path(args.target_path).glob("*.huf"))) == 2:
print(ps)
for p_idx in range(len(ps)):
if "coder" in ps[p_idx].stem:
cp_idx = p_idx
else:
assert False, f"{Fore.RED}无效的路径,没有找到压缩文件{Style.RESET_ALL}"
print(f"开始解压 {args.target_path}")
if args.v:
print(decode(huf_path=ps[1-cp_idx], coder_path=ps[cp_idx])[-1].print_code_table(verbose=False))
else:
decode(huf_path=ps[1-cp_idx], coder_path=ps[cp_idx], verbose=False)
print("解压完成")
else:
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
m = QtGUIHuff()
m.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == "__main__":
main(parse_args())
5. 运行实例
A. GIF版演示
这里先放一个gif图片(比较大,44兆,不知道能不能加载出来),高清版本去下面的B站视频里看看

B. B站高清版
视频链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1cL41177zL/
6. 完整代码
完整代码如下
A. huff.py
import sys
import pickle
import argparse
import itertools
import collections
from pathlib import Path
from heapq import heapify, heappush, heappop
from typing import Union, Any, Dict, List, Tuple
from PyQt5.QtCore import QDir
import pandas
import pandas as pd
from colorama import Fore, Style
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
__author__ = "Jack Wang"
__date__ = "2021/12/19"
sys.path.append(Path(__file__).resolve().parent.joinpath("./ui").__str__())
class _EOFSymbol:
"""
Notes:
_EOFSymbol 是内置的文件结尾的类,用于在编码的时候标志文件的结尾。
由于在进行哈夫曼树的构建的时候需要选出来权最小的节点,因此需要重写比较的魔术方法。
默认文档结尾是频率最少的字符,因此和任何数字比较
"""
def __repr__(self):
return "_EOF"
def __lt__(self, other):
return True
def __gt__(self, other):
return False
def __eq__(self, other):
return self.__class__ == other.__class__
def __hash__(self):
return hash(self.__class__)
_EOF = _EOFSymbol()
def _guess_concat_function(data):
"""
Notes:
To support multiple types of input, e.g., str, bytes, list, there must be a
function that return the needed concat function
Returns:
pass
"""
return {type(u""): u"".join, type(b""): bytes}.get(type(data), list)
def ensure_dir(path: Union[str, Path]) -> Path:
path: Path = path if isinstance(path, Path) else Path(path)
if not path.exists():
path.mkdir(parents=True)
assert path.is_dir()
return path
class _HuffmanCoder:
"""
Notes:
_HuffmanCoder, which provide encode, decode, serialize, deserialize, save_code, load_code functionalities.
Args:
"""
def __init__(self, code_table: Dict[Any, Tuple[int, int]], concat=list, check=True, eof=_EOF):
"""
Notes:
initialize method of _HuffmanCoder with given code table
Args:
code_table (Dict[Any, Tuple[int, int]]): code table of all symbols in the encoding sequence, create automatically by
HuffmanCoderFactory, items are Tuple[Symbol, [depth, bit]]
concat: concat method of symbols, will be automatically determined in HuffmanCoderFactory
check: valid code table's format
eof: eof symbol, leave it alone
"""
self._table = code_table
self._concat = concat
self._eof = eof
if check:
assert isinstance(self._table, dict), f"{Fore.RED}Code table need to be a dict!{Style.RESET_ALL}"
assert all(
isinstance(b, int) and b >= 1 and isinstance(v, int) and v >= 0 for (b, v) in self._table.values()
), f"{Fore.RED}Code table internal format Error!{Style.RESET_ALL}"
def get_code_table(self) -> Dict[Any, Tuple[int, int]]:
"""
Notes:
get_code_table returns code table of input sequence
Returns:
self._table
"""
return self._table
def print_code_table(self, verbose=False) -> pandas.DataFrame:
"""
Notes:
print_code_table is used to print code table
Args:
verbose (bool): if True, then print the table in a pretty format
Returns:
pd.DataFrame
"""
pd.options.display.max_rows = None
columns = list(zip(*list(zip(*itertools.chain(
[("Symbol", "Huff Code", "BitSize")], (
(repr(symbol), bin(val)[2:].rjust(bits, "0"), str(bits))
for symbol, (bits, val) in self._table.items()
)
)))))
df = pd.DataFrame(columns[1:], columns=columns[0])
if verbose:
print(df)
return df
def _encode_streaming(self, raw_sequence):
size = 0
buffer = 0
for s in raw_sequence:
bits, values = self._table[s]
buffer = (buffer << bits) + values
size += bits
while size >= 8:
byte = buffer >> (size - 8)
yield byte
buffer = buffer - (byte << (size - 8))
size -= 8
if size > 0:
bit, value = self._table[self._eof]
buffer = (buffer << bit) + value
size += bit
if size > 8:
byte = buffer >> (size - 8)
else:
byte = buffer << (8 - size)
yield byte
def _decode_streaming(self, encoded_sequence):
# Reverse lookup table: map (bitsize, value) to symbols
lookup = {(b, v): s for s, (b, v) in self._table.items()}
buffer = 0
size = 0
for byte in encoded_sequence:
for m in [128, 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1]:
buffer = (buffer << 1) + bool(byte & m)
size += 1
if (size, buffer) in lookup:
symbol = lookup[size, buffer]
if symbol == self._eof:
return
yield symbol
buffer = 0
size = 0
def encode(self, raw_seq):
"""
Notes:
encode is used to encode the sequence that build the huffman tree
Args:
raw_seq: sequence that build the huffman tree
Returns:
bytes
"""
return bytes(self._encode_streaming(raw_seq))
def decode(self, encoded_seq, concat=None):
return (concat or self._concat)(self._decode_streaming(encoded_seq))
def save(self, path: Union[str, Path], metadata: Any = None):
code_table = self.get_code_table()
data = {
"code_table": code_table,
"type": type(self),
"concat": self._concat,
}
if metadata:
data['metadata'] = metadata
path = Path(path)
ensure_dir(path.parent)
with path.open(mode='wb') as f:
pickle.dump(data, file=f)
@staticmethod
def load(path: Union[str, Path]) -> '_HuffmanCoder':
path = Path(path)
with path.open(mode='rb') as f:
data = pickle.load(f)
cls = data['type']
assert issubclass(cls, _HuffmanCoder)
code_table = data['code_table']
return cls(code_table, concat=data['concat'])
class HuffmanCoderFactory(_HuffmanCoder):
"""
Notes:
HuffmanCodecFactory is the class that create HuffmanCoder from different type of inputs
Methods:
from_frequencies: create HuffmanCoder from frequency table
"""
@classmethod
def from_frequencies(cls, frequencies: Dict[Any, int], concat=None, eof=_EOF):
"""
Notes:
from_frequencies creates huffman codec by symbol-frequency table/mapping.
Args:
frequencies (Dict[Any, int]): Symbols and its frequency, symbols can be str, bytes or int, etc.
concat (Union[None]): concat method of symbols, will be determined by the function if argument is not
specified
eof (_EOFSymbol): leave it alone.
Returns:
__HuffmanCoder
Examples:
>>> huf_coder = HuffmanCoderFactory.from_frequencies({"a":29, "b":10, "c": 5})
>>> type(huf_coder)
"""
concat_function = concat if concat is not None else _guess_concat_function(next(iter(frequencies)))
# build huffman tree node heap
# each item: (frequency, [(symbol, (bitsize, value))], value equals which layer of the tree
heap: List[Tuple[int, List[Tuple[Any, Tuple[int, int]]]]] = [(freq, [(symbol, (0, 0))]) for symbol, freq in
frequencies.items()]
# add eof
if eof not in frequencies:
heap.append((1, [(eof, (0, 0))]))
heapify(heap)
while len(heap) > 1:
# get first 2 min as left and right child tree
a: Tuple[int, List[Tuple[Any, Tuple[int, int]]]] = heappop(heap)
b: Tuple[int, List[Tuple[Any, Tuple[int, int]]]] = heappop(heap)
# merge child to form parent
# parent frequencies adds together, left child add 0 ahead (do nothing) of previous bits
# right add 1 ahead of previous bits
merged = (
a[0] + b[0],
[(s, (n + 1, v)) for (s, (n, v)) in a[1]] + [(s, (n + 1, (1 << n) + v)) for (s, (n, v)) in b[1]]
)
heappush(heap, merged)
# code table is root
table = dict(heappop(heap)[1])
return cls(table, concat=concat, check=False, eof=eof)
@classmethod
def from_sequence(cls, sequence: Union[List[Any], Tuple[Any], str, bytes]):
"""
Notes:
from_sequence will build a huffman tree from a sequence of symbol
Args:
sequence (Union[List, Tuple][Any]):
Returns:
__HuffmanCoder
Examples:
>>> seq = "a"*100 + "b"*29 + "c"*32
>>> coder = HuffmanCoderFactory.from_sequence(seq)
"""
frequencies = collections.Counter(sequence)
return cls.from_frequencies(frequencies, concat=_guess_concat_function(sequence))
def encode(path: Union[str, Path], verbose: bool=True):
assert (path := Path(path)).exists(), f"{Fore.RED}{path} not exists!{Style.RESET_ALL}"
with path.open(mode="rb") as f:
content = f.read()
coder = HuffmanCoderFactory.from_sequence(content)
byte = coder.encode(content)
if not (out_fd := path.resolve().parent / (path.stem + "_huf")).exists():
out_fd.mkdir(parents=True)
with (main_path := out_fd.joinpath(path.stem + "_" + path.suffix[1:] + ".huf")).open("wb") as f:
f.write(byte)
coder.save(coder_path := out_fd.joinpath(path.stem + "_coder.huf"))
b1 = path.stat().st_size
b2 = main_path.stat().st_size
b3 = coder_path.stat().st_size
summary1, summary2, summary3, summary4 = [""]*4
if verbose:
summary1 = f"Origin file: {path.stem}{path.suffix}, byte size: {b1}"
summary2 = f"Compressed file: {main_path.stem}{main_path.suffix}, byte size: {b2}"
summary3 = f"HuffCoder file: {coder_path.stem}{coder_path.suffix}, byte size: {b3}"
summary4 = f"{Fore.GREEN}Compression rate {b2}/{b1}={Style.BRIGHT}{round(b2/b1, 4)*100}%{Style.NORMAL}" +\
f", saved {Style.BRIGHT}{b1-b2}{Style.RESET_ALL} bytes"
print(s := "Summary".center(max([len(summary1), len(summary2), len(summary3), len(summary4)]), "="))
print("\n".join((summary1, summary2, summary3, summary4)))
print("="*len(s))
return b1, b2, b3, coder
def decode(huf_path: Union[Path, str], coder_path: Union[Path, str], verbose: bool=True):
huf_path, coder_path = Path(huf_path), Path(coder_path)
coder = _HuffmanCoder.load(coder_path)
with huf_path.open(mode="rb") as f:
content = f.read()
decoded = coder.decode(content)
with (dec_path := huf_path.parent.joinpath((s := huf_path.stem.split("_"))[0] + f"_decode.{s[1]}")).open(mode="wb") as f:
f.write(decoded)
b1 = huf_path.stat().st_size
b2 = coder_path.stat().st_size
b3 = dec_path.stat().st_size
if verbose:
summary1 = f"Origin file: {huf_path.stem}{huf_path.suffix}, byte size: {b1}"
summary2 = f"Coder file: {coder_path.stem}{coder_path.suffix}, byte size: {b2}"
summary3 = f"Decompressed file: {dec_path.stem}{dec_path.suffix}, byte size: {b3}"
summary4 = f"{Fore.GREEN}Decompression rate {b3}/{b1}={Style.BRIGHT}{round(b3/b1, 4)*100}%{Style.NORMAL}" +\
f", lost {Style.BRIGHT}{b3-b1}{Style.RESET_ALL} bytes"
print(s := "Summary".center(max([len(summary1), len(summary2), len(summary3), len(summary4)]), "="))
print("\n".join((summary1, summary2, summary3, summary4)))
print("="*len(s))
return b1, b2, b3, coder
def parse_args() -> argparse.Namespace:
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description="哈夫曼压缩算法Python实现,可以对任意文件进行压缩,提供命令行以及GUI用户界面。作者:Jack Wang"
)
parser.add_argument("-s", "--src", dest="src_path", type=str, default=None, help="需要压缩的文件路径")
parser.add_argument("-t", "--target", dest="target_path", type=str, default=None, help="需要解压文件所在的文件夹的路径")
parser.add_argument("-v", "--verbose", dest="v", action="store_true", help="是否显示压缩的摘要信息")
parser.add_argument("-g", "--gui", dest="gui", action="store_true", help="是否以GUI方式显示")
return parser.parse_args()
class QtGUIHuff(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
from Ui_main import Ui_Form
self.ui = Ui_Form()
self.ui.setupUi(self)
self.setWindowTitle("哈夫曼压缩/解压缩程序")
self.ui.compress.clicked.connect(self.compress)
self.ui.decompress.clicked.connect(self.decompress)
def fileDialog(self):
dialog = QFileDialog()
dialog.setFileMode(QFileDialog.AnyFile)
dialog.setFilter(QDir.Files)
if dialog.exec():
filename = dialog.selectedFiles()
return Path(filename[0])
else:
return False
def compress(self):
f_path = self.fileDialog()
self.ui.textEdit.setReadOnly(True)
s = ["开始压缩"]
self.ui.textEdit.setText("\n".join(s))
result = encode(f_path)
summary1 = f"Origin file: {f_path.stem}{f_path.suffix}, byte size: {result[0]}"
summary2 = f"Compressed file: byte size: {result[1]}"
summary3 = f"HuffCoder file: , byte size: {result[2]}"
summary4 = f"Compression rate {result[1]}/{result[0]}={round(result[1]/result[0], 4)*100}%" + \
f", saved {result[0] - result[1]} bytes"
self.ui.textEdit.setText("\n".join([*s, summary1, summary2, summary3, summary4, "压缩结束"]))
self.ui.textEdit_2.setText(result[-1].print_code_table(verbose=False).__str__())
def decompress(self):
f_path = self.fileDialog()
if f_path.suffix != ".huf":
QMessageBox.warning(self, "警告", "请选择正确的压缩文件路径", QMessageBox.Yes, QMessageBox.Yes)
return False
if len(ps := list(Path(f_path).parent.glob("*.huf"))) == 2:
print(ps)
for p_idx in range(len(ps)):
if "coder" in ps[p_idx].stem:
cp_idx = p_idx
else:
QMessageBox.warning(self, "警告", "缺少必要的解压缩文件", QMessageBox.Yes, QMessageBox.Yes)
return False
s = ["开始解压"]
import time
time.sleep(1)
self.ui.textEdit.setText("\n".join(s))
result = decode(huf_path:=ps[1-cp_idx], coder_path:=ps[cp_idx])
summary1 = f"Origin file: {huf_path.stem}{huf_path.suffix}, byte size: {result[0]}"
summary2 = f"Coder file: {coder_path.stem}{coder_path.suffix}, byte size: {result[1]}"
summary3 = f"Decompressed file: byte size: {result[2]}"
summary4 = f"Decompression rate {result[2]}/{result[0]}={round(result[2]/result[0], 4)*100}%" +\
f", lost {result[2] - result[0]} bytes"
self.ui.textEdit.setText("\n".join([*s, summary1, summary2, summary3, summary4, "解压结束"]))
self.ui.textEdit_2.setText(result[-1].print_code_table(verbose=False).__str__())
def main(args: argparse.Namespace):
if not args.gui:
assert 0 < int(args.src_path is not None) + int(args.target_path is not None), f"{Fore.RED}请选择压缩或者解压,使用-h查询用法{Style.RESET_ALL}"
if not args.gui:
print(f"{Fore.GREEN}命令行工作模式{Style.RESET_ALL}")
if args.src_path is not None:
print(f"开始压缩 {args.src_path}")
if args.v:
print(encode(Path(args.src_path))[-1].print_code_table(verbose=False))
else:
encode(Path(args.src_path), verbose=False)
print("压缩完成")
elif args.target_path is not None:
if len(ps := list(Path(args.target_path).glob("*.huf"))) == 2:
print(ps)
for p_idx in range(len(ps)):
if "coder" in ps[p_idx].stem:
cp_idx = p_idx
else:
assert False, f"{Fore.RED}无效的路径,没有找到压缩文件{Style.RESET_ALL}"
print(f"开始解压 {args.target_path}")
if args.v:
print(decode(huf_path=ps[1-cp_idx], coder_path=ps[cp_idx])[-1].print_code_table(verbose=False))
else:
decode(huf_path=ps[1-cp_idx], coder_path=ps[cp_idx], verbose=False)
print("解压完成")
else:
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
m = QtGUIHuff()
m.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == "__main__":
main(parse_args())
2. Ui_main.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Form implementation generated from reading ui file '/media/jack/JackCode/project/data_structure/11_huffman/ui/main.ui'
#
# Created by: PyQt5 UI code generator 5.9.2
#
# WARNING! All changes made in this file will be lost!
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
class Ui_Form(object):
def setupUi(self, Form):
Form.setObjectName("Form")
Form.resize(751, 374)
self.layoutWidget = QtWidgets.QWidget(Form)
self.layoutWidget.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(50, 20, 641, 321))
self.layoutWidget.setObjectName("layoutWidget")
self.horizontalLayout_2 = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout(self.layoutWidget)
self.horizontalLayout_2.setContentsMargins(0, 0, 0, 0)
self.horizontalLayout_2.setObjectName("horizontalLayout_2")
self.verticalLayout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
self.verticalLayout.setObjectName("verticalLayout")
self.horizontalLayout = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout()
self.horizontalLayout.setObjectName("horizontalLayout")
self.compress = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.layoutWidget)
self.compress.setObjectName("compress")
self.horizontalLayout.addWidget(self.compress)
self.decompress = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.layoutWidget)
self.decompress.setObjectName("decompress")
self.horizontalLayout.addWidget(self.decompress)
self.verticalLayout.addLayout(self.horizontalLayout)
self.label = QtWidgets.QLabel(self.layoutWidget)
self.label.setAlignment(QtCore.Qt.AlignCenter)
self.label.setObjectName("label")
self.verticalLayout.addWidget(self.label)
self.textEdit = QtWidgets.QTextEdit(self.layoutWidget)
self.textEdit.setObjectName("textEdit")
self.verticalLayout.addWidget(self.textEdit)
self.horizontalLayout_2.addLayout(self.verticalLayout)
self.verticalLayout_2 = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
self.verticalLayout_2.setObjectName("verticalLayout_2")
self.label_2 = QtWidgets.QLabel(self.layoutWidget)
self.label_2.setAlignment(QtCore.Qt.AlignCenter)
self.label_2.setObjectName("label_2")
self.verticalLayout_2.addWidget(self.label_2)
self.textEdit_2 = QtWidgets.QTextEdit(self.layoutWidget)
self.textEdit_2.setObjectName("textEdit_2")
self.verticalLayout_2.addWidget(self.textEdit_2)
self.horizontalLayout_2.addLayout(self.verticalLayout_2)
self.retranslateUi(Form)
QtCore.QMetaObject.connectSlotsByName(Form)
def retranslateUi(self, Form):
_translate = QtCore.QCoreApplication.translate
Form.setWindowTitle(_translate("Form", "Form"))
self.compress.setText(_translate("Form", "压缩"))
self.decompress.setText(_translate("Form", "解压"))
self.label.setText(_translate("Form", "Compress/Decompress Log"))
self.label_2.setText(_translate("Form", "Huffman Tree"))